The retina holds immense importance in our visual perception. Routine retinal exams help preserve the longevity and clarity of this pivotal sensory hub. Positioned at the rear of the eye, the retina plays a crucial role in how we see things. Getting regular retinal checkups as part of your eye assessments is vital for maintaining good vision. By incorporating regular retinal exams into your routine eye checkups, you help eye care specialists detect any changes early on, allowing for better care of your eyes and vision health.
What Is the Retina?
Your retina is a thin layer of tissue lining the back of your eye. It captures light that enters your eye and sends signals to your brain, enabling you to see. Without a healthy retina, clear vision is impossible, making it a vital part of your eye’s anatomy.
The retina contains millions of cells, including rods and cones, which are responsible for detecting light and colour. When light hits these cells, it creates electrical signals that are sent to the brain through the optic nerve. A damaged retina can lead to vision loss, so keeping it in good health is crucial.
Understanding how your retina works helps you appreciate the importance of regular retinal exams. These exams can detect issues that might otherwise go unnoticed, making early intervention possible.
Why Are Retinal Exams Important?
One of the most important aspects of a retinal exam is its ability to detect underlying health conditions. Because the retina is part of the central nervous system, changes in its appearance can indicate systemic health issues.
For example, high blood pressure can cause changes in the blood vessels of your retina. Similarly, diabetes can lead to diabetic retinopathy, where high blood sugar levels damage retinal blood vessels. Early detection through a retinal exam can help manage these conditions before they worsen.
Not only do retinal exams detect eye-related issues, but they can also provide clues to other health problems. This makes them an invaluable tool for comprehensive health monitoring.
What Conditions Can a Retinal Exam Detect?
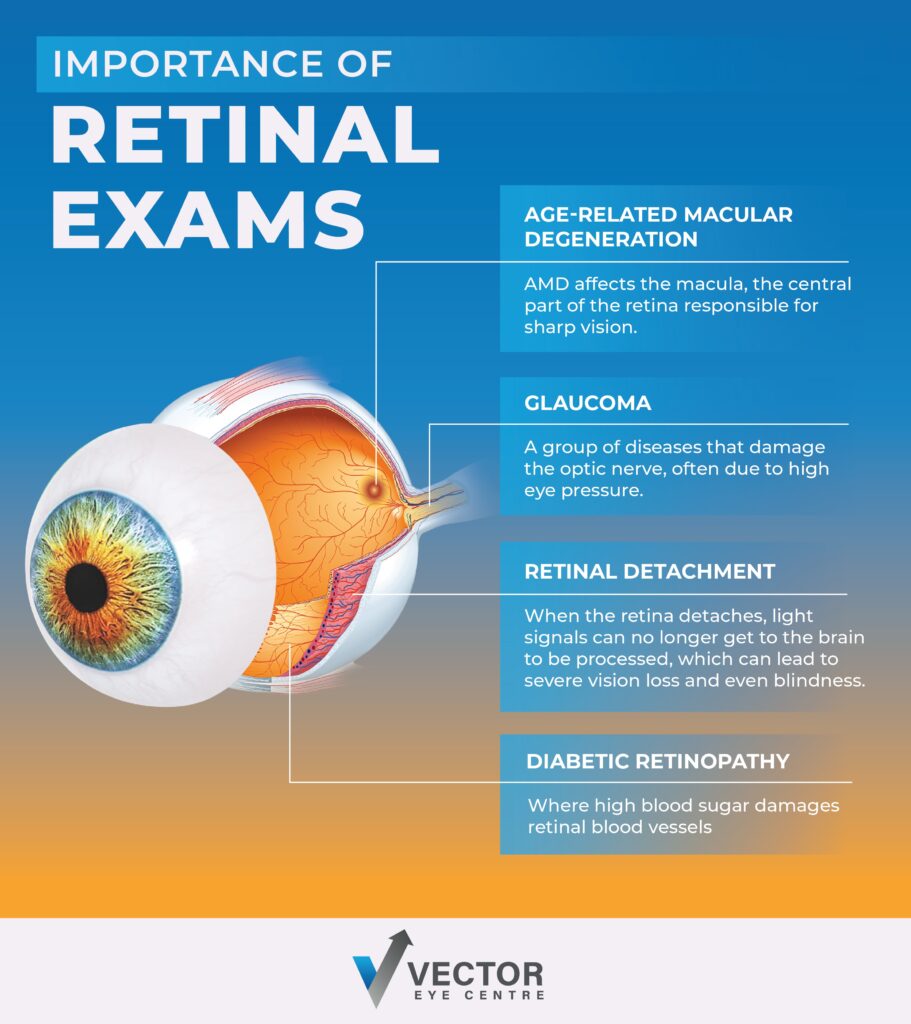
Retinal exams can identify a variety of eye and health conditions, including diabetic eye disease, age-related macular degeneration, glaucoma, and more.
Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetes patients are at risk of developing diabetic retinopathy, where high blood sugar damages retinal blood vessels. It often goes unnoticed until vision loss occurs, which is why early detection is important to prevent significant vision loss.
Age-Related Macular Degeneration
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) affects the macula—the central part of the retina responsible for sharp vision—and is the leading cause of blindness in North America for adults over 50. As it can develop both slowly and rapidly, detecting AMD early can help slow its progression and maintain vision quality.
Glaucoma
Glaucoma refers to a group of diseases that damage the optic nerve, often due to high eye pressure. The most common type of glaucoma, primary open-angle glaucoma, presents no symptoms early on. Therefore, early detection through retinal exams is important to help prevent severe vision loss.
Retinal Detachment
A retinal exam can detect early signs of a retinal detachment, such as tears or holes, allowing for prompt treatment. When the retina detaches, light signals can no longer get to the brain to be processed, which can lead to severe vision loss and even blindness. Prompt treatment is necessary to preserve vision.
These are just a few examples, but they illustrate why regular retinal exams are vital for maintaining your eye health and overall well-being.
Regular Retinal Exam vs. Dilated Retinal Exam
You might wonder how a regular retinal exam differs from a dilated one. While both are important, they are slightly different.
A dilated eye exam involves using special eye drops to widen (dilate) your pupils, allowing your ophthalmologist to see the back of your eye more clearly. Similarly to regular retinal exams, dilations help ophthalmologists diagnose conditions like AMD, glaucoma, and diabetic retinopathy in individuals who may have smaller pupils or are at a greater risk of developing eye diseases.
Not everyone may require a dilated retinal exam on each visit as they may not always be required each time. Your ophthalmologist considers factors like your age and health before deciding on the necessity of dilating your pupils.
What Does a Retinal Exam Entail?
A retinal exam involves several steps and technology to provide a thorough assessment. Here’s what you may experience during a retinal exam:
- Preparation: Your ophthalmologist’s assistants will ask about your medical history and any vision issues. They may use eye drops to dilate your pupils, allowing for a better view of your retina.
- Imaging: Advanced imaging tools, like ocular coherence tomography (OCT) and fundus cameras, capture detailed images of your retina. These images help identify any abnormalities.
- Evaluation: Your ophthalmologist will examine the images for signs of conditions like diabetic retinopathy, AMD, and glaucoma. They’ll discuss their findings with you and recommend any necessary treatments.
- Follow-up: Based on the results, your ophthalmologist may schedule follow-up appointments to monitor your retinal health and make sure any treatments are effective.
My Results Are Normal, Now What?
If you have been in for a retinal exam in the past, that’s great! You are taking steps to protect your eye health. However, attending follow-up appointments and going in when you are next due is a part of that process.
Creating a baseline using retinal images allows healthcare professionals to establish a reference point for an individual’s eye health. The images obtained from the initial exam serve as a baseline or starting point for tracking any changes in the retina over time. Healthcare providers analyze these images to identify any abnormalities, signs of eye conditions, or systemic health issues.
In follow-up retinal exams conducted in subsequent years, new retinal images are captured and compared to the baseline images. Eye doctors examine these images to detect any alterations, progression of eye diseases, or development of new conditions. A comparison between the baseline images and current images helps in detecting subtle changes that may indicate early stages of eye diseases like diabetic retinopathy, AMD, or glaucoma. Any deviations from the baseline may trigger further evaluation and appropriate interventions.
Establishing a baseline through retinal images and using them for comparative analysis in subsequent years enables eye doctors to track changes, provide personalized care, and ultimately help preserve vision and overall eye health.
Protect Your Retina
Regular retinal exams are essential for maintaining eye health and detecting underlying health conditions early. By understanding the importance of these exams and following recommended guidelines, you can protect your vision and your overall health.
Don’t wait for vision problems to arise—take proactive steps to protect your retina. Your vision is priceless, and regular retinal exams are a small investment in preserving it for years to come.



